In this article, we are going to talk about the importance of R value. You may not be familiar with the topic, so let’s start with some basics first.
Thank you for reading this post, don't forget to subscribe!What Is Insulation?
Insulation is an important factor that makes your home comfortable and energy efficient. Insulation is also called the “unsung hero” of the home. You don’t see it and rarely think about it. There are plenty of insulation types, and all of them are made differently. Just to mention, some different materials are spray foam insulation, fiberglass, and foam board insulation. There are also a number of other different forms of applying insulation such as batting and blown in.
Adding Insulation to your home provides resistance to heat flow and lowers your heating and cooling bills. Insulating your home properly not only reduces heating and cooling costs but also improves comfort.
What Is The R value?
R value measures the resistance of heat transfer from one side of an object to another. For example, one inch of solid wood has an R value of 1. In comparison, an inch of blown fiberglass insulation has an R value of 3.1 – 3.4, and an inch of closed cell spray foam insulation has an R value of 6. R value is an indicator of how well insulated your building is. It refers to the ability for a material to resist heat loss. Said differently, the higher the R value, the greater the resistance, and better insulation power.
How Insulation Works?
To understand how insulation works first, you need to understand heat flow, which involves three basic mechanisms:
- Conduction
- Convection
- Radiation
The movement of heat through materials is called conduction. The transfer of heat through liquids and gases is called convection. Radiant heat travels in a straight line and heats anything solid in its path that absorbs energy.
Usually, insulation materials work by slowing conductive heat flow and to a lesser extent convective heat flow. Radiant heat gain is reduced by radiant barriers and reflective insulation systems. For efficiency, the reflective surface must face an air space. This is how heat flows from warmer to cooler spaces until there is no longer a temperature difference. This means that in winter, heat flows directly from all heated living spaces to adjacent unheated attics, garages, basements, and the whole property is affected. Heat flow also moves indirectly through ceilings, walls, floors, and whenever there’s a difference in temperature between environments. During cold weather, heat flows from the interior of the house to the outdoors. To retain comfort, the heat lost during winter must be replaced by your heating system, and the heat gained during summer must be removed by your cooling system. Insulating your home properly will decrease this heat flow by providing an effective resistance to the flow of heat.
R Values For Each Insulation Type
The resistance of an insulating material to conductive heat flow is rated in terms of its thermal resistance – R value. The higher the R value means that the material has higher insulating power. The R value depends on the type of insulation, its density, and its thickness. There are some materials whose R value also depends on temperature, moisture accumulation, and aging. Let’s take a look at R values of different materials and depths.
R Value Of Materials And Depths
| Material | R-value/in | 3 1/2″ | 5 1/4″ | 10″ | 12″ | 15″ |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Fiberglass (batt) | 3.1 – 3.4 | 10.8 – 11.9 | 16.3 – 17.8 | 31.0 – 34.0 | 37.2 – 40.8 | 46.5 – 51.0 |
| Fiberglass blown (attic) | 2.2 – 4.3 | 7.7 – 15.0 | 11.5 – 22.6 | 22.0 – 43.0 | 26.4 – 51.6 | 33.0 – 64.5 |
| Fiberglass blown (wall) | 3.7 – 4.3 | 12.9 – 15.0 | 19.4 – 22.6 | 37.0 – 43.0 | 44.4 – 51.6 | 55.5 – 64.5 |
| Mineral Wool (batt) | 3.1 – 3.4 | 10.8 – 11.9 | 16.3 – 17.8 | 31.0 – 34.0 | 37.2 – 40.8 | 46.5 – 51.0 |
| Mineral Wool blown (attic | 3.1 – 4.0 | 10.8 – 14.0 | 16.3 – 21.0 | 31.0 – 40.0 | 37.2 – 48.0 | 46.5 – 60.0 |
| Mineral Wool blown (wall) | 3.1 – 4.0 | 10.8 – 14.0 | 16.3 – 21.0 | 31.0 – 40.0 | 37.2 – 48.0 | 46.5 – 60.0 |
| Cellulose blown (attic) | 3.2 – 3.7 | 11.2 – 12.9 | 16.8 – 15.0 | 32.0 – 37.0 | 38.4 – 44.4 | 48.0 – 55.5 |
| Cellulose blown (wall) | 3.8 – 3.9 | 13.3 – 13.6 | 19.9 – 20.8 | 38.0 – 39.0 | 45.6 – 46.8 | 57.0 – 58.5 |
| Polystrene Board | 3.8 – 5.0 | 13.3 – 17.5 | 19.9 – 26.2 | 38.0 – 50.0 | 45.6 – 60.0 | 57.0 – 75.0 |
| Polyurethane Board | 5.5 – 6.5 | 19.2 – 22.7 | 28.9 – 34.1 | 55.0 – 65.0 | 66.0 – 78.0 | 82.5 – 97.5 |
| Polyisocyanurate (foil-faced) | 5.6 – 8.0 | 18.2 – 28.0 | 29.4 – 42.0 | 56.0 – 80.0 | 67.2 – 96.0 | 84.0 – 120.0 |
| Open Cell Spray Foam | 3.5 – 3.6 | 12.2 – 12.6 | 18.4 – 18.9 | 35.0 – 36.0 | 42.0 – 43.2 | 52.5 – 54.0 |
| Closed Cell Spray Foam | 6.0 – 6.5 | 21.0 – 22.7 | 31.5 – 34.1 | 60.0 – 65.0 | 72.0 – 78.0 | 90.0 – 97.5 |
Table 1. R value and depths of material.
The resistance of an insulating material to conductive heat flow is rated in terms of its thermal resistance – R value. The higher the R value means that the material has higher insulating power. The R value depends on the type of insulation, its density, and its thickness. There are some materials whose R value also depends on temperature, moisture accumulation, and aging. Let’s take a look at R values of different materials and depths.
This way, the insulation that fills building cavities densely enough to reduce airflow can also reduce convective heat loss. Different from traditional insulation materials, radiant barriers are highly reflective materials that re-emit radiant heat rather than absorbing it, reducing cooling loads. Even if it is possible to calculate an R value for a specific radiant barrier or reflective insulation installation, the effectiveness of these systems does not reflect the real ability to reduce heat gain by reflecting heat from the living space. Factors such as climate, the type of heating and cooling system, and the part of the house you plan to insulate define the amount of insulation or R value you’ll need. To learn more, see our information on adding insulation to an existing house or insulating a new house. You should also remember that air sealing and moisture control are important to home energy efficiency and health.
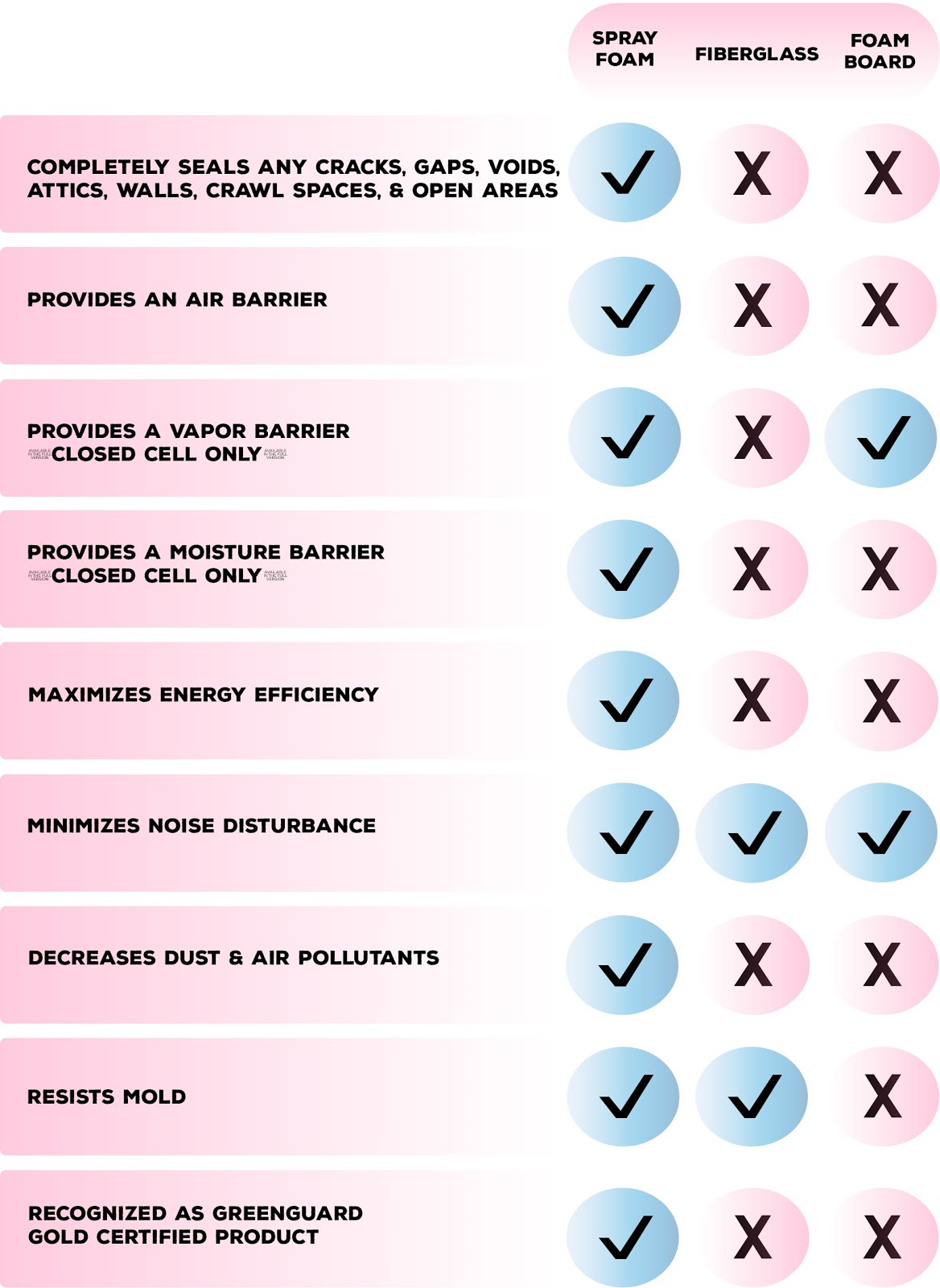
Best Insulation Material / Type
When it comes to choosing the right insulation material for your home, you will come across a bunch of options, and doing some research is never a bad idea. The table below reflects the qualities of the three most-used insulation materials.
We Do Spray Foam Insulation
Spray foam creates an air barrier that acts as the first line of defense against not only radon but also other malignant gases. Besides this, spray foam is a vapor barrier that protects the foundation. It protects a building from major damages that can occur over time. At Solve Insulation, we are committed to helping our customers understand the how and why of their home renovations so that you feel confident when choosing our services. We invest our time in your home protection. For knowing more about insulation and its benefits, keep reading our informative posts. Our services might fit the needs of your home renovation or insulation project.
If you find your home in need of insulation, get in touch. Call us at 646 809 1007 or 917 900 1155 or email us at info@solveinsulation.us to book a free consultation.
